Understanding Merge Sort
7 min read
Breakdown:
Sorting algorithms are foundational in computer science, and Merge Sort is one of the most efficient and widely used. It’s especially favored for its predictable O(n log n) time complexity and its elegant use of recursion.
In this blog post, we’ll break down how Merge Sort works and implement it in Python, Java, and Rust.
What is Merge Sort?
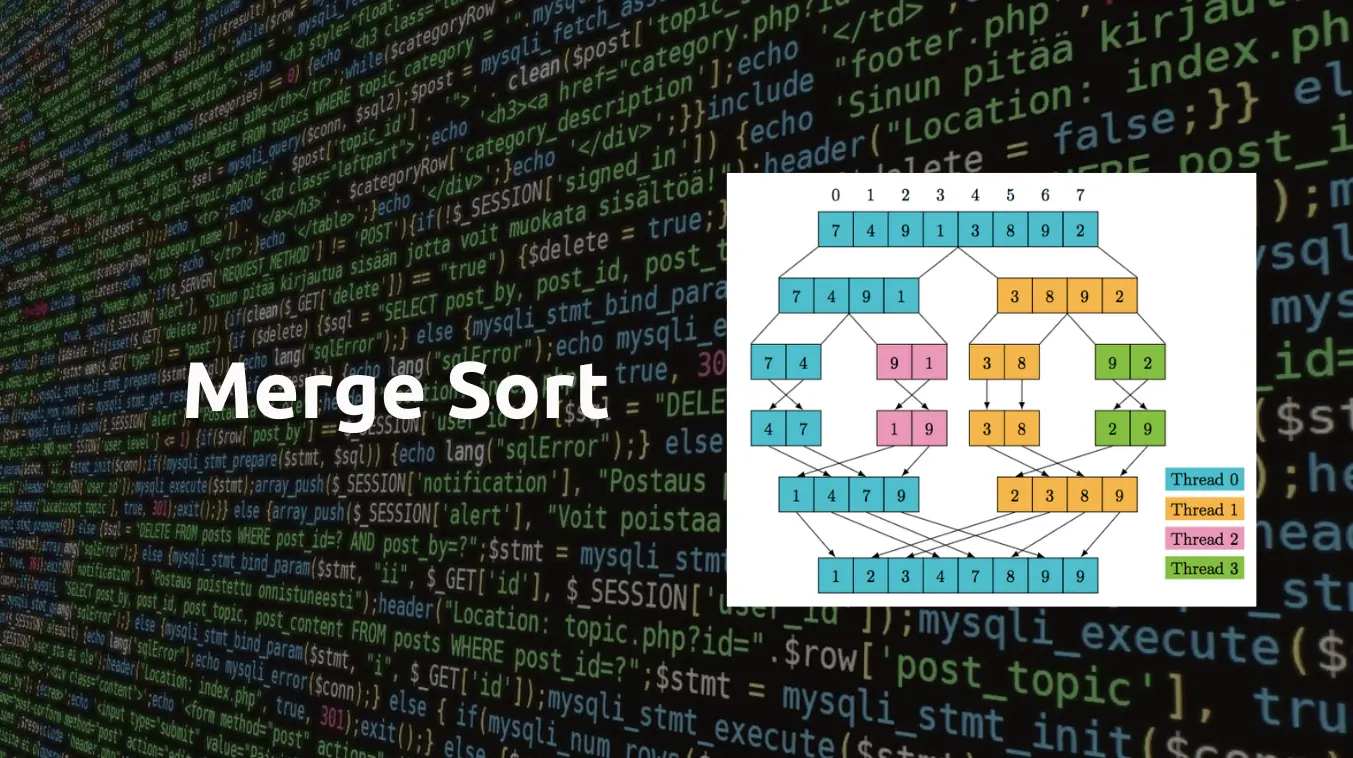
Merge Sort is a divide-and-conquer algorithm:
-
Divide the input array into two halves.
-
Recursively sort both halves.
-
Merge the two sorted halves into a single sorted array.
Key Properties:
-
Time Complexity: O(n log n) in all cases (best, average, worst)
-
Space Complexity: O(n) due to the temporary arrays used for merging
-
Stable Sort: Maintains the relative order of equal elements
How Merge Sort Works (Step-by-Step)
Suppose we want to sort: [38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10]
- Divide it into halves:
- [38, 27, 43] and [3, 9, 82, 10]
- Keep splitting:
- [38], [27], [43] and [3], [9], [82], [10]
- Merge and sort:
- [27, 38], [27, 38, 43], [3, 9], [10, 82], [3, 9, 10, 82]
- Final merge:
- [3, 9, 10, 27, 38, 43, 82]
Examples:
Merge Sort in Python
def merge_sort(arr):
if len(arr) > 1:
mid = len(arr) // 2
left_half = arr[:mid]
right_half = arr[mid:]
merge_sort(left_half)
merge_sort(right_half)
i = j = k = 0
# Merging the halves
while i < len(left_half) and j < len(right_half):
if left_half[i] < right_half[j]:
arr[k] = left_half[i]
i += 1
else:
arr[k] = right_half[j]
j += 1
k += 1
# Copy remaining elements
while i < len(left_half):
arr[k] = left_half[i]
i += 1
k += 1
while j < len(right_half):
arr[k] = right_half[j]
j += 1
k += 1
# Example
arr = [38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10]
merge_sort(arr)
print(arr)
Merge Sort in Java
public class MergeSort {
public static void mergeSort(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
mergeSort(arr, left, mid);
mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, right);
merge(arr, left, mid, right);
}
}
private static void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right) {
int n1 = mid - left + 1;
int n2 = right - mid;
int[] L = new int[n1];
int[] R = new int[n2];
for (int i = 0; i < n1; ++i)
L[i] = arr[left + i];
for (int j = 0; j < n2; ++j)
R[j] = arr[mid + 1 + j];
int i = 0, j = 0;
int k = left;
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (L[i] <= R[j]) {
arr[k++] = L[i++];
} else {
arr[k++] = R[j++];
}
}
while (i < n1) arr[k++] = L[i++];
while (j < n2) arr[k++] = R[j++];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10};
mergeSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
for (int val : arr) {
System.out.print(val + " ");
}
}
}
Merge Sort in Rust
fn merge_sort(mut arr: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
if arr.len() <= 1 {
return arr;
}
let mid = arr.len() / 2;
let left = merge_sort(arr[..mid].to_vec());
let right = merge_sort(arr[mid..].to_vec());
merge(left, right)
}
fn merge(left: Vec<i32>, right: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut merged = Vec::with_capacity(left.len() + right.len());
let mut i = 0;
let mut j = 0;
while i < left.len() && j < right.len() {
if left[i] <= right[j] {
merged.push(left[i]);
i += 1;
} else {
merged.push(right[j]);
j += 1;
}
}
merged.extend_from_slice(&left[i..]);
merged.extend_from_slice(&right[j..]);
merged
}
fn main() {
let arr = vec![38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10];
let sorted = merge_sort(arr);
println!("{:?}", sorted);
}
Conclusion
Merge Sort is a powerful sorting technique that balances speed and stability. It’s a great choice when you need predictable performance and can afford a bit of extra space. Whether you’re coding in Python for scripting, Java for enterprise applications, or Rust for performance-critical tasks, Merge Sort fits right in.
More Articles
Key Words:
Pythonrustjava merge sortalgorithm